Table Of Content

(This is discussed in more detail below.) If you used the simplified method to claim home office deductions on your return, you don't have to worry about this. A second home is generally defined as a property that you live in for part of the year, and that isn't primarily a rental property. For example, if you have a condo at the beach that you live in for two months every summer and also rent out for a month during the summer season, it is likely considered to be a second home.
How to Use Market Losses to Reduce Your Taxes
The tax rules applicable to short sales differ depending on whether the debt is recourse or nonrecourse. Let’s say you and your spouse bought a home for $150,000 many years ago in a non-community property state, and it is worth $980,000 on the date the first of you dies. The survivor’s tax basis in the home jumps to $565,000 (his or her half of the original $150,000 basis plus half of the deceased spouse’s $980,000 date-of-death value). Before we go any further, it's important to mention the concept of cost basis since it's used to determine your potential tax liability. However, there are certain criteria you must meet to qualify for the home sale exclusion. There are also several exceptions to the 121 exclusion rules.

Use Your Capital Losses
See Worksheet 3, later, for assistance in determining your taxable gain. If a federal estate tax return (Form 706) was filed or required to be filed, the value of the property listed on the estate tax return is your basis. If Form 706 didn’t have to be filed, your basis in the home is the same as its appraised value at the date of death, for purposes of state inheritance or transmission taxes. The Eligibility Test determines whether you are eligible for the maximum exclusion of gain ($250,000 or $500,000 if married filing jointly). You may take the exclusion, whether maximum or partial, only on the sale of a home that is your principal residence, meaning your main home.
How Much Tax Do I Pay When Selling My House?
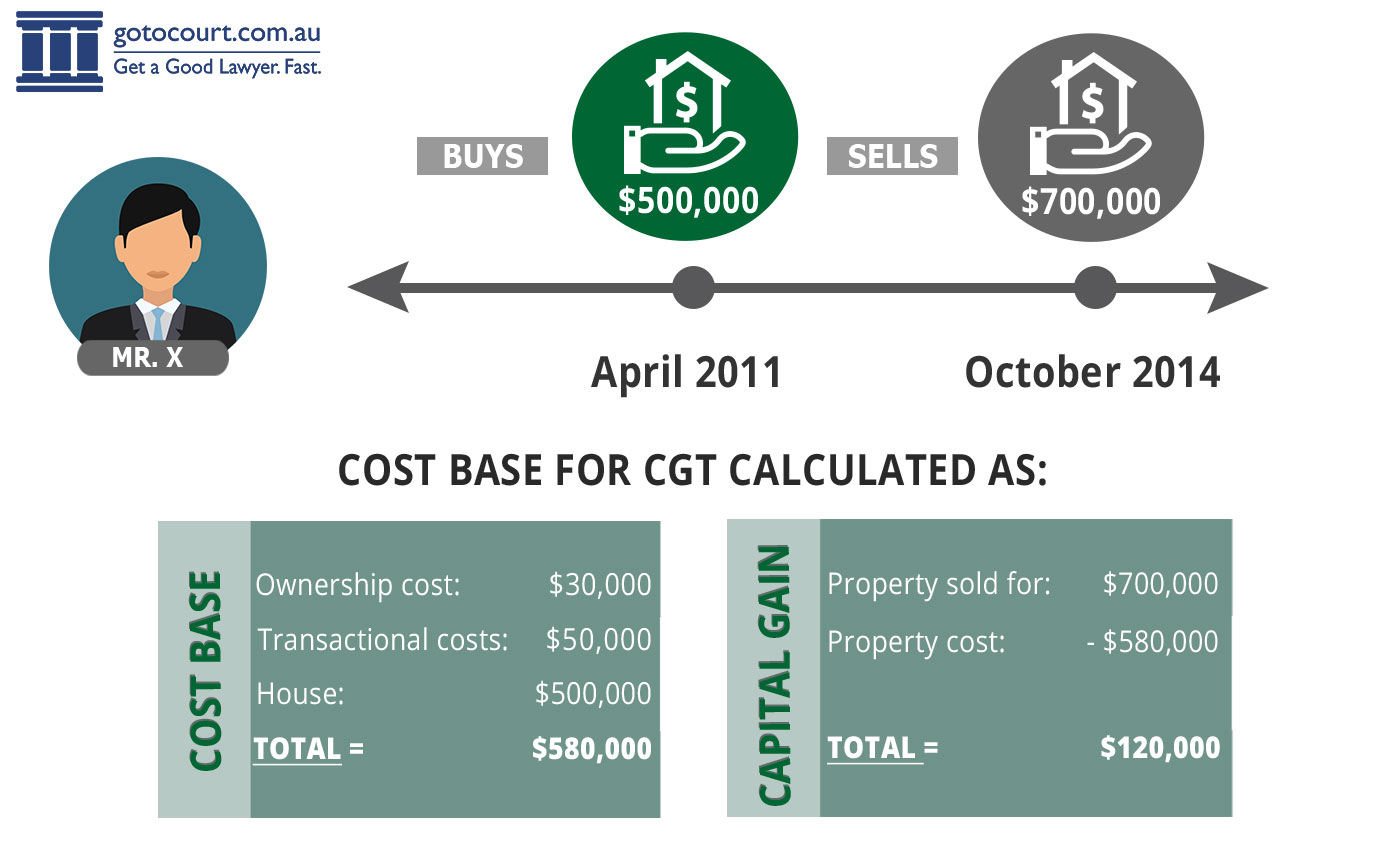
For tax purposes, these dates are calculated from the day after the original purchase to the date of sale of the property. This is considered a capital improvement because the renovation increases the overall value of your home. That’s $150,000 (the original purchase price) + $50,000 (the amount spent on the capital improvement).
Capital Gains Tax Explained (What It Is & How to Avoid Capital Gains Tax)
How to avoid capital gains tax on real estate - SFGATE
How to avoid capital gains tax on real estate.
Posted: Fri, 21 Jul 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The home values in your area have shot up like crazy, so you were able to sell your home for $900,000! Let’s say Mom and Dad bought the family home years ago for $100,000, and it’s worth $1 million when it’s left to you. When you sell, your purchase price (or “basis”) is not the $100,000 your folks paid, but instead the $1 million it’s worth on the last parent’s date of death.
Use Capital Losses to Offset Gains
You may be able to report any non-excludable gain on an installment basis. If NONE of the three bullets above is true, you don’t need to report your home sale on your tax return. If you didn’t make separate home and business calculations on your property, skip to Reporting Deductions Related to Your Home Sale, later. Gain from the sale or exchange of your main home isn’t excludable from income if it is allocable to periods of nonqualified use. Nonqualified use means any period after 2008 where neither you nor your spouse (or your former spouse) used the property as your main home, with certain exceptions.
Exceptions to Capital Gains Taxes
This publication explains the tax rules that apply when you sell or otherwise give up ownership of a home. If you meet certain conditions, you may exclude the first $250,000 of gain from the sale of your home from your income and avoid paying taxes on it. The exclusion is increased to $500,000 for a married couple filing jointly. Fortunately, there are ways to reduce or avoid capital gains taxes on a home sale altogether. The IRS offers a few scenarios to avoid capital gains taxes when selling your house.
If you qualify for an exclusion on your home sale, up to $250,000 ($500,000 if married and filing jointly) of your gain will be tax free. If your gain is more than that amount, or if you qualify only for a partial exclusion, then some of your gain may be taxable. This section contains step-by-step instructions for figuring out how much of your gain is taxable.
What are capital gains and losses?
Rosen said taxpayers who are wondering what to do with properties should seek professional assistance. Mark Weisleder, a senior partner at Real Estate Lawyers.ca LLP, said that when people pass away, some of their assets are considered "sold" on their date of death. The best choice will depend on several factors, such as the basis price of shares or units that were purchased and the amount of gain that will be declared. Some categories of assets get different capital-gains tax treatment than the norm. This is not an offer to buy or sell any security or interest. Working with an adviser may come with potential downsides such as payment of fees (which will reduce returns).
If you didn’t meet the Eligibility Test, then your home isn’t eligible for the maximum exclusion, but you should continue to Does Your Home Qualify for a Partial Exclusion of Gain. You can include the sale of vacant land adjacent to the land on which your home sits as part of a sale of your home if ALL of the following are true. Also, you may be able to increase your exclusion amount from $250,000 to $500,000. You may take the higher exclusion if you meet all of the following conditions. If any of these conditions are true, the exclusion doesn’t apply. Your home sale isn’t eligible for the exclusion if ANY of the following are true.
Stacey creates three copies of Worksheet 2 and titles them “Business or Rental,”“Home,” and “Total” to allocate basis and the amount realized for the different uses of the property. The total you get on line 7 on your “Business” copy of Worksheet 2 is the gain or loss related to the business or rental portion of the property you sold. Treatment of any gain also depends on the use during the 5 years leading up to the sale. To figure the portion of the gain allocated to the period of nonresidential use, see Business or rental usage calculations, later.
You must report all 1099-B transactions on Schedule D (Form 1040), Capital Gains and Losses and you may need to use Form 8949, Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets. This is true even if there's no net capital gain subject to tax. You own shares in the mutual fund but the fund owns capital assets, such as shares of stock, corporate bonds, government obligations, etc. One of the ways the fund makes money for you is to sell these assets at a gain.
For example, if you are transferring a home to a spouse or ex-spouse the IRS doesn’t consider that to be a gain or a loss. Real estate gift tax applies any time an individual transfers property to someone without receiving full market value in return. If you own your own home, you might be able to save on your tax returns. Get the most value from your home with these eight tax deductions. “In essence, you’re swapping one investment asset for another,” says White. He cautions, however, that there are very strict rules regarding timelines and guidelines with this transaction, so be sure to check them with an accountant.
Although the residential real estate market has been up and down lately, your property has likely increased in value since you purchased it. Eventually, when you dispose of the property, either voluntarily or involuntarily, you'll need to determine the federal income tax consequences concerning that built-in appreciation. A short-term capital gain is the result of selling a capital asset you held in your possession for one year or less. Long-term capital gains are capital assets held for more than a year.
To qualify as your primary residence, the IRS requires that you prove the property was your main home where you lived most of the time. You’ll need to show that you owned the home for at least two years and lived in the property as your primary residence for at least two of the five years immediately preceding the sale. One way to delay the tax hit on all or part of the otherwise taxable capital gains is to use the proceeds you get from your insurance company to buy a new home within four years of the disaster.
If you don't satisfy the holding period requirement and sell the stock for less than the purchase price, your loss is a capital loss but you still may have ordinary income. If your capital losses exceed your capital gains, you can use it to offset up to $3,000 of ordinary income. If your losses exceed your gains by more than $3,000, any excess will carry over into future years. Individuals, estates and trusts with income above specified levels own this tax on their net investment income. If you have net investment income from capital gains and other investment sources, and a modified adjusted gross income above the levels listed below, you will owe the tax.

No comments:
Post a Comment